ADLs vs IADLs are more than just medical terms — they represent the small yet powerful actions that define our independence. Imagine being unable to bathe, dress, or cook your own meal. These everyday tasks, often taken for granted, shape our dignity and quality of life. In healthcare, they are vital measures of how well a person can live and function independently.
This guide will clearly explain ADLs vs IADLs, their key differences, and why they matter for seniors, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
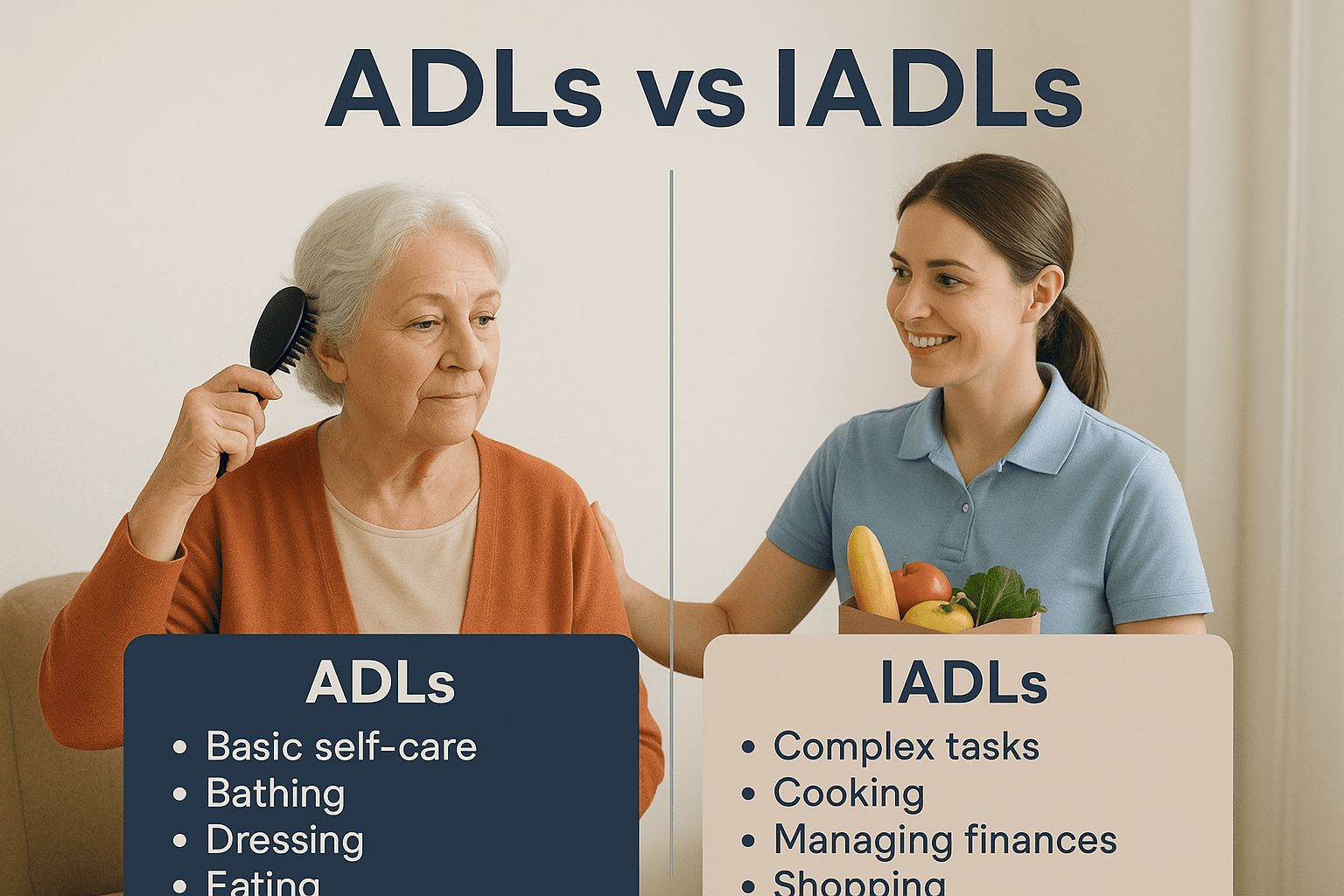
🧩 What Are ADLs in the ADLs vs IADLs Comparison?
Contents
- 1 🧩 What Are ADLs in the ADLs vs IADLs Comparison?
- 2 🧩 What Are ADLs (Activities of Daily Living) in the ADLs vs IADLs Comparison?
- 3 🏡 What Are IADLs (Instrumental Activities of Daily Living) in ADLs vs IADLS?
- 4 🧠 ADLs vs IADLs: Key Differences
- 5 🩺 Why ADLs vs IADLs Matter in Senior Care
- 6 👩⚕️ How Caregivers Can Support ADLs and IADLs
- 7 ALSO READ
- 8 🌿 Real-Life Example:
- 9 🧾 Summary
- 10 💬 FAQs: ADLs vs IADLs
- 11 REFERENCES
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) are basic self-care tasks that every person performs to maintain physical health and hygiene. These tasks show how well someone can manage fundamental daily functions.
Examples of ADLs include:
- Bathing: Washing and keeping oneself clean.
- Dressing: Selecting and wearing appropriate clothing.
- Eating: Feeding oneself independently.
- Toileting: Managing bathroom needs.
- Transferring: Moving safely from bed to chair or walking.

🧩 What Are ADLs (Activities of Daily Living) in the ADLs vs IADLs Comparison?
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) are basic self-care tasks that every person performs to maintain physical health and hygiene. These tasks show how well someone can manage fundamental daily functions.
Examples of ADLs include:
- Bathing: Washing and keeping oneself clean.
- Dressing: Selecting and wearing appropriate clothing.
- Eating: Feeding oneself independently.
- Toileting: Managing bathroom needs.
- Transferring: Moving safely from bed to chair or walking.
Healthcare providers assess ADLs to determine how much physical assistance or rehabilitation a person might need.
🏡 What Are IADLs (Instrumental Activities of Daily Living) in ADLs vs IADLS?
In the ADLs vs IADLs framework, Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs) represent the complex tasks that allow a person to live independently in the community.
Common IADLs include:
- Cooking and meal preparation
- Cleaning and housekeeping
- Managing finances
- Using transportation
- Shopping for groceries or clothes
- Managing medications
- Using communication tools (phone, email, etc.)
IADLs go beyond physical ability — they reflect planning, problem-solving, and cognitive skills. Losing IADL abilities is often an early sign of declining independence.
🧠 ADLs vs IADLs: Key Differences
| Feature | ADLs | IADLs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Basic personal care activities | Complex skills for independent living |
| Focus | Physical self-care | Cognitive and social functioning |
| Examples | Bathing, dressing, eating | Cooking, managing money, cleaning |
| Assessment Use | Measures physical ability | Evaluates independence level |
| Who Needs Help | People with mobility or health issues | People with cognitive decline or aging adults |
In short, ADLs measure physical capability, while IADLs measure independent living skills.
🩺 Why ADLs vs IADLs Matter in Senior Care
Understanding ADLs vs IADLs is essential for creating personalized care plans. It helps caregivers and families:
- Identify specific support needs early
- Prevent long-term functional decline
- Promote independence and safety
For example, an elderly person may manage ADLs like bathing and eating but struggle with IADLs such as managing finances or transportation. Recognizing this distinction allows for targeted support that maintains dignity and confidence.
👩⚕️ How Caregivers Can Support ADLs and IADLs
Supporting independence doesn’t mean taking over tasks completely — it’s about empowering individuals to do what they can.
Caregiver tips:
- Encourage participation: Let seniors choose their clothes or help in meal prep.
- Use adaptive tools: Grab bars, shower chairs, and easy-grip utensils improve safety.
- Establish routines: Consistent schedules build confidence and reduce confusion.
- Monitor changes: Decline in IADLs often signals the need for medical evaluation.
A proactive approach can delay dependence and improve emotional well-being.
ALSO READ
Is Walking or Running Better for Weight Loss?
🌿 Real-Life Example:
Mrs. Khan, an 80-year-old living alone, can still bathe, dress, and eat without help (ADLs). However, she forgets to pay bills and struggles to cook (IADLs).
With caregiver support twice a week, she maintains independence — a perfect example of balancing both ADLs and IADLs for aging with dignity.
🧾 Summary
Understanding ADLs vs IADLs is crucial for caregivers, families, and healthcare professionals.
ADLs reflect basic physical independence, while IADLs show functional and cognitive capability.
By assessing both, we can provide the right support — ensuring seniors live safely, confidently, and with dignity.
💬 FAQs: ADLs vs IADLs
Q1. What does ADL mean in healthcare?
A. ADL stands for Activities of Daily Living, the basic self-care tasks like eating, bathing, and dressing.
Q2. How are IADLs different from ADLs?
A. IADLs are more complex skills, such as managing money or cooking, which help people live independently.
Q3. Who assesses ADLs and IADLs?
A. Nurses, occupational therapists, and caregivers often use standardized tools to evaluate daily functioning.
Q4. Why are ADLs and IADLs important for the elderly?
A. They help identify the level of independence, track health decline, and plan appropriate home or medical care.
Q5. Can someone need help with IADLs but not ADLs?
A. Yes. Many older adults can handle personal care but may struggle with complex tasks like managing medications or finances.
REFERENCES
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/666768
https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2011-21299-001
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/activities-of-daily-living-adls
https://www.aota.org/advocacy/advocacy-news/coding/~/media/391EBF0C2F39446E908A525CA22272B0.ashx