Mindfulness based cognitive therapy helps reduce stress, anxiety, and overthinking.
Developed by Dr. Zindel Segal, Dr. Mark Williams, and Dr. John Teasdale, MBCT blends mindfulness with cognitive tools. As a result, people learn to respond clearly instead of reacting quickly.
Over the last twenty years, hospitals, universities, and clinics have used MBCT. Moreover, research in journals such as The Lancet and JAMA Psychiatry shows clear benefits. Therefore, many clinicians now recommend MBCT for emotional balance and relapse prevention.
Many people report one early change: they learn to watch a thought rather than get trapped in it. Consequently, they feel
Contents
What Is Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy?
Mindfulness based cognitive therapy (MBCT) is an 8-week program. It teaches simple skills to calm the mind and handle emotions better. In addition, it provides structured tools that work for beginners.
First, it uses mindfulness training. You notice sensations and thoughts without judging them.
Next, it adds cognitive strategies. You learn how thoughts shape feelings and how to interrupt harmful thinking
Thus, MBCT helps with:
- Anxiety
- Chronic stress
- Repetitive negative thinking
- Low mood
- Sleep trouble
Overall, MBCT gives practical tools that most people can learn.
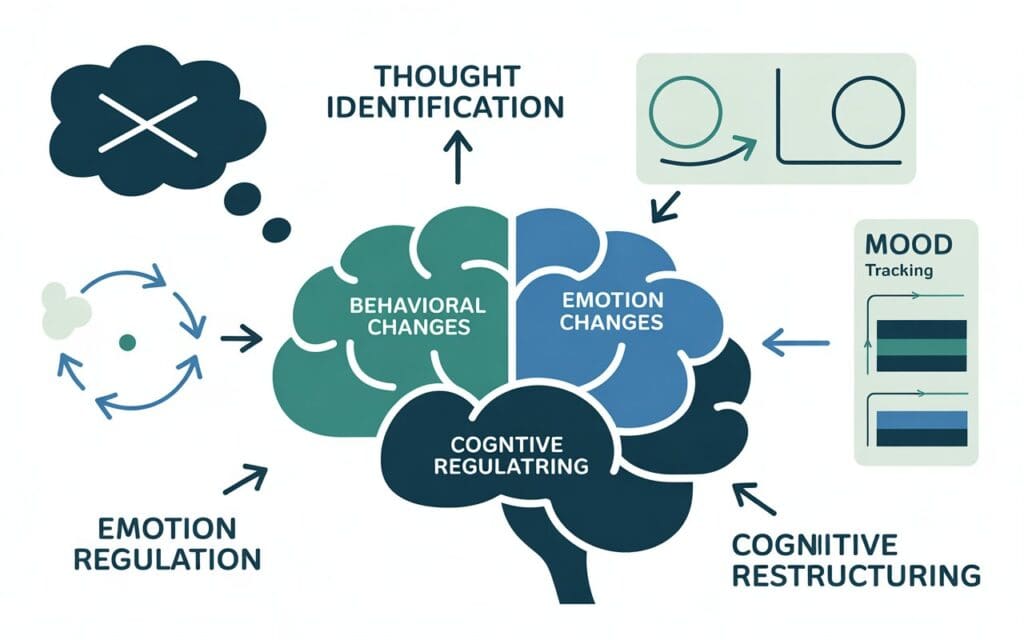
How MBCT Works: The Science Explained
The mind often runs on autopilot. Thoughts arrive fast, and then feelings follow. MBCT changes that pattern.
It uses three clear steps:
1. Awareness
First, you learn to notice thoughts as they appear and pass. This step reduces the feeling of being controlled by thoughts.
2. Breathing & Body Grounding
Then, you use slow, steady breathing to calm the nervous system. This improves focus and lowers stress.
3. Cognitive Understanding
Finally, you spot unhelpful thoughts early. That stops emotional spirals before they grow.
Together, these steps create a small pause. In that pause you can choose a calmer response.
Evidence-Based Benefits of MBCT
Clinical studies show several benefits. For example, MBCT can:
- Reduce stress and worry. In addition, it slows rapid thinking.
- Improve mood stability. Research indicates lower relapse rates for depression.
- Strengthen attention. Simple practices sharpen concentration.
- Support better sleep. A calmer mind falls asleep more easily.
- Build emotional resilience. Over time, you stay steadier in hard moments.
Therefore, students, professionals, and caregivers often find MBCT helpful.
Simple MBCT Techniques for Daily Life
Here are some techniques taught in MBCT programs.
1. Three-Minute Breathing Space
A quick reset during busy or stressful moments.
Steps:
- Notice current thoughts and feelings.
- Shift attention to slow breathing.
- Relax the body and stay present.
Psychologists describe this as a “mini pause button” for the mind.
2. Body Scan Meditation
Attention moves gently through the body, from head to toe.
This reduces tension, increases awareness, and builds relaxation.
3. Thought Labeling
When a thought appears, it is gently labeled as:
- “Worry”
- “Planning”
- “Memory”
- “Fear”
Labeling decreases emotional intensity and creates distance from the thought.
4. Mindful Daily Activities
Simple tasks like walking, eating, or showering are done with full presence.
This teaches the brain to stay grounded throughout the day.
Who Can Benefit the Most?
MBCT helps people who face:
- Repeated negative thinking
- High work stress
- Emotional sensitivity
- Trouble sleeping
- Difficulty focusing
Because of its gentle nature, MBCT fits beginners and can be paired with other treatments.
Conclusion
In short, mindfulness based cognitive therapy gives clear, research-backed tools. With consistent practice, you gain calm, clarity, and emotional balance. Eventually, these small moments of awareness turn into long-term resilience.
FAQs
Q1. What is mindfulness-based cognitive therapy?
MBCT is a therapeutic approach combining mindfulness practices with cognitive therapy to help prevent relapse of depression and manage stress by observing thoughts without judgment.
Q2,How is MBT different from CBT?
MBT focuses on awareness and acceptance of thoughts, while CBT emphasizes changing negative thought patterns.
Q3. What is an example of mindfulness-based therapy?
A common example is mindful breathing exercises used to observe and release stressful thoughts in the moment.
Q4. What’s the difference between CBT and MBCT?
CBT changes thinking patterns, whereas MBCT trains the mind to notice and accept thoughts, reducing emotional reactivity
.Q5. Can MBCT be practiced at home?
Yes. Breathing exercises, body scans, and mindful moments can all be done at home without special tools.





